Search Results
Results for: 'metabolically active cells'
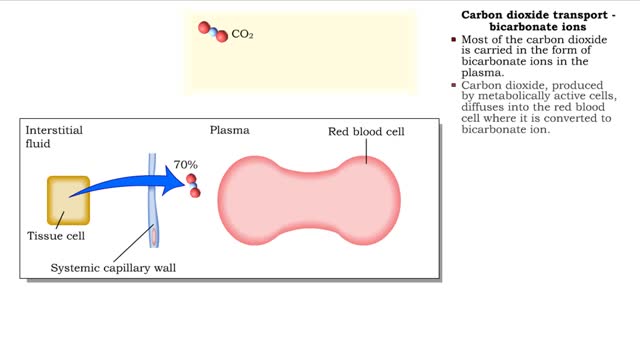
Methods of carbon dioxide transport - carbaminohemoglobin and bicarbonate ions
By: HWC, Views: 6685
• Carbon dioxide is transported three ways: • As bicarbonate ions in the plasma. • Bound to hemoglobin. • As a dissolved gas in the plasma. • A small percent of carbon dioxide is transported as a dissolved gas. • Some of the carbon dioxide is bound to hemoglobin, in the fo...
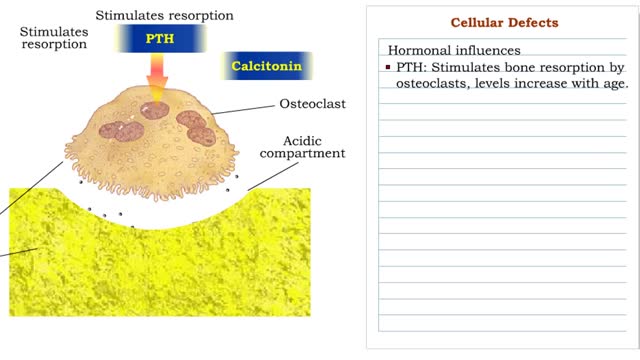
Cellular Defects - Osteoblasts, Osteoclasts and Osteocytes
By: HWC, Views: 6301
■ Metabolically active bone-building cells that secrete astroid. ■ Cover surfaces of newly formed bone and respond to growth stimuli ■ Less responsive to growth factors as the body ages. ■ Contribute to hone loss once their reproductive and biosynthetic potential lessens....
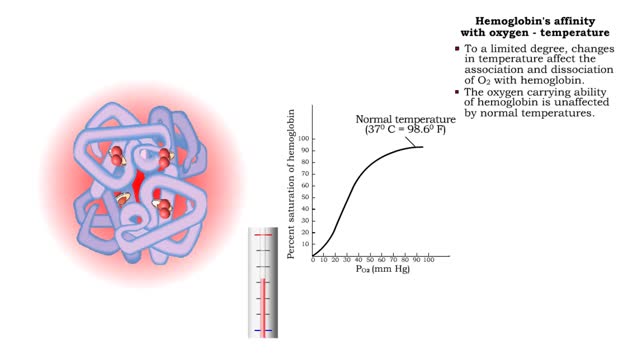
Hemoglobin's affinity with oxygen - carbon dioxide, temperature and bisphosphoglycerate (BPG)
By: HWC, Views: 6773
• The carbon dioxide gas is temporarily converted to carbonic acid in red blood cells by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, and then further converted to hydrogen and bicarbonate ions. • The result of increased carbon dioxide is decreased pH causing the Bohr effect. • Elevated carbon dioxid...
By: HWC, Views: 7171
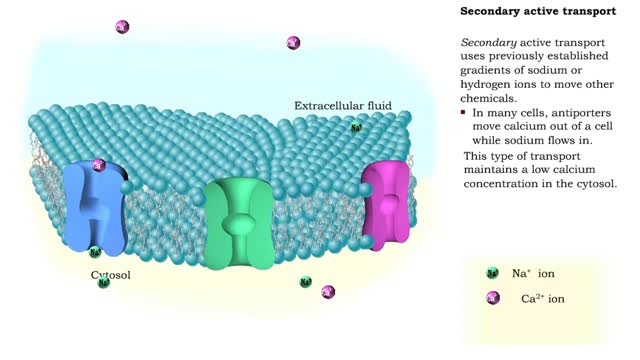
Energy stored (in a hydrogen or sodium concentration gradient) is used to drive other substances against their own concentration gradients Secondary active transport, is transport of molecules across the cell membrane utilizing energy in other forms than ATP. In many cells, antiporters mov...
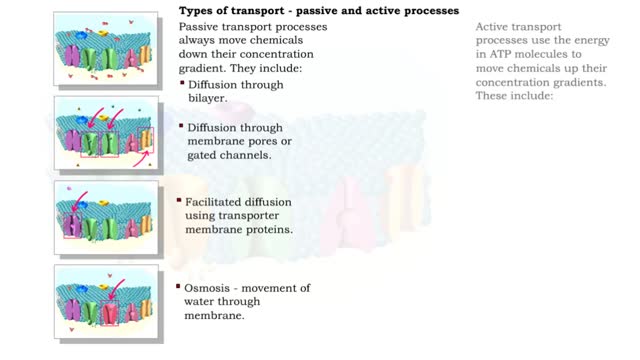
Type of Transport - Active and Passive Processes
By: HWC, Views: 6866
Active transport moves materials from lower to a higher concentration, while passive transport moves materials from higher to lower concentration. Active transport requires energy to proceed, while passive transport does not require the input of extra energy to occur. Transport processes that ...
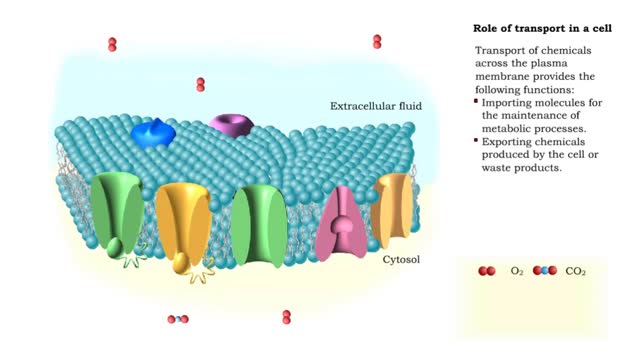
By: HWC, Views: 6793
Transport of chemicals across the plasma membrane provides the following functions: Importing molecules for the maintenance of metabolic processes. Exporting chemicals produced by the cell or waste products. Communicating with other cells, allowing for the generation and conduction of a...
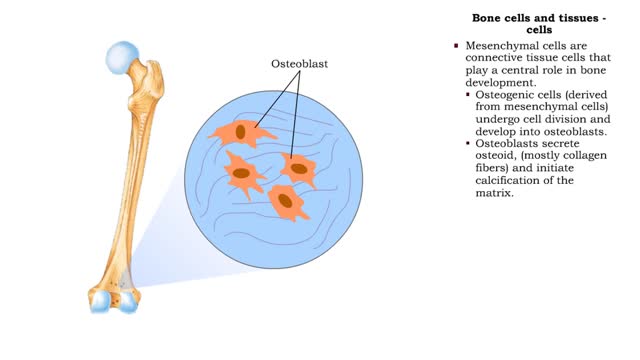
Bone cells and tissues - tissue composition and cells
By: HWC, Views: 7418
Bone tissue consists of bone cells secreting bone matrix. • The extracellular bone matrix is a connective tissue that is hard, yet flexible. • Collagen fibers provide flexibility. • Inorganic mineral salts (primarily calcium phosphate, or hydroxyapatite) provide hardness. • Togethe...
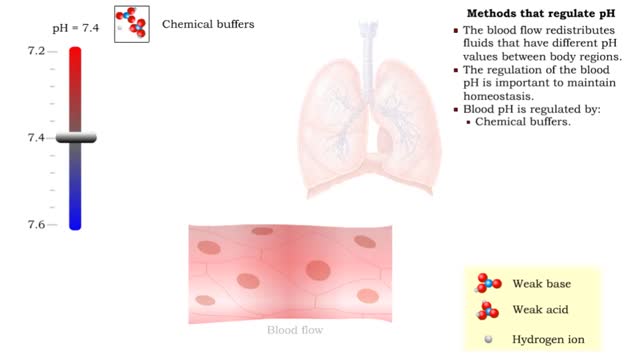
By: HWC, Views: 6812
• The blood flow redistributes fluids that have different pH values between body regions. • The regulation of the blood pH is important to maintain homeostasis. • Blood pH is regulated by: • Chemical buffers. • The respiratory system. • The urinary system. • All thes...
Bone processes - resorption and deposition, remodeling and response to stress in adult bones
By: HWC, Views: 6913
• The process of remodeling bone tissues involves bone cells resorbing or depositing minerals into bone tissue. • During resorption, bone cells break down bone tissue and release calcium and other minerals for use by other cells in the body. • Bone cells also rebuild bone tissue by depo...
Advertisement